Blog » Coaching Models and Techniques » The Self-Efficacy Theory
The Self-Efficacy Theory
For many people, self-doubt and uncertainty can be roadblocks that prevent us from achieving our aspirations. Fortunately, psychologists have come up with the self-efficacy theory which explains why some individuals do eventually succeed while others stay stuck in their doubt and limitation.

This blog post will provide an introduction to the self-efficacy theory, examining its history, implications, and more. Regardless of their knowledge level on the subject matter, newbies, or experienced professionals looking for additional information, readers should come out of this article with a better understanding of how self-efficacy works in various areas of life.
Let’s get started!
What is the Self-Efficacy Theory
The Self-Efficacy Theory, developed by Stanford University psychologist Albert Bandura in 1971, posits that a person’s behavior and beliefs are both influenced by his or her level of confidence.
“Self-efficacy theory suggests that a person’s belief in their ability to succeed in a specific task or situation influences their behavior, motivation, and achievement.”
The theory suggests that people draw from their past successes and experiences to create a belief system about the likelihood of success in any given activity.
By believing in their ability to achieve desirable outcomes, individuals find the necessary motivation to take on self-improvement tasks and set realistic goals for themselves.
This innate motivation for improvement is what drives people to focus on growth and development both personally and professionally, leading to improved outcomes in a wide range of activities.
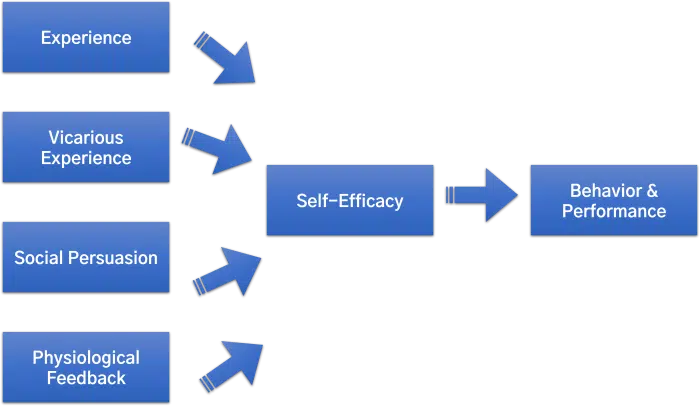
The self-efficacy theory beliefs can be influenced by four main factors according to this theory: past experiences, vicarious experiences where individuals observe others completing related tasks or achieving outcomes, verbal persuasion, and physiological cues such as mental state or arousal level.
This theory suggests that people with relatively higher levels of self-efficacy tend to perform better than those with lower levels of self-efficacy.
Consequently, understanding and improving the self-efficacy beliefs held by individuals continues to be an important focus for researchers investigating the nature of human behavior.
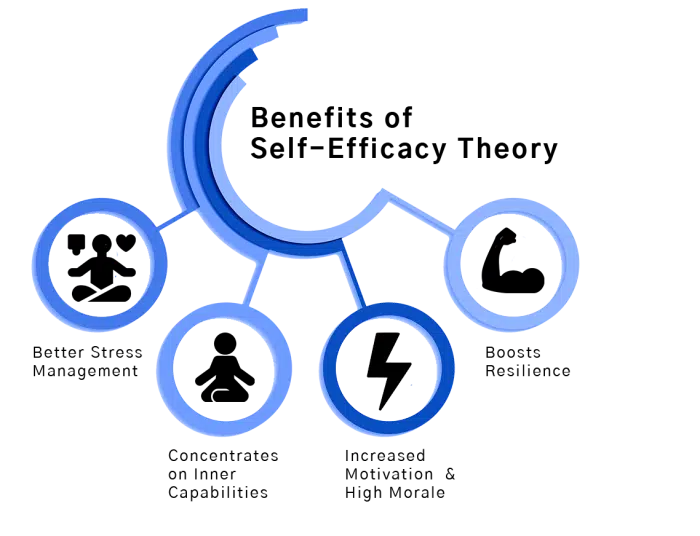
Benefits of Self-Efficacy Theory
There are many beneficial results of self-efficacy theory in the fields of psychology, education, and health.
- Concentrates on Inner Capabilities
It proposes that how people think about their capabilities affects how they act and the outcomes which result from those self-determined goals. People with greater confidence in their abilities learn more efficiently, persist longer in their tasks, and show better performance on cognitive tasks.
- Better Stress Management
Research has also suggested that viewing yourself as someone with a high degree of efficacy helps with stress management and avoidance of depression. This feeling of control and mastery enables constructive strategies to be used to face difficult life challenges.
Are you someone who struggles with stress management? If so, check out these 14 Stress Management Apps to Relax Your Mind & Body. I’m sure you will find these tools useful.
- Increased Motivation and High Morale
Individuals who perceive themselves as efficacious have been found to have increased motivation for studying and positive academic achievement. Therefore, this versatile theory has great potential for helping people reach their fullest potential in any area of life whether it is regarding physical health or psychological well-being
- Boosts resilience
Another benefit of self-efficacy theory is that it can enhance individuals’ resilience in the face of adversity. By believing in their abilities to overcome obstacles, individuals with high self-efficacy are more likely to persevere and bounce back from setbacks.
Limitations of Self-Efficacy Theory
Self-efficacy theory has been an important concept in psychology for decades, but it does contain certain limitations.
- Does not account for environmental factors
This theory does not effectively account for environmental factors. It looks at individuals in isolation and often fails to consider situations where external factors can play a role in determining feelings of self-efficacy.
- Accuracy of the theory is not well established
While effective goal completion is a strong predictor of higher self-efficacy, completing difficult tasks can also have adverse effects on personal beliefs about one’s capabilities. This implies that the accuracy of the theory varies greatly depending on individual behavior and circumstances.
- Difficult to measure subjective aspects of behavior
It can be difficult to accurately measure feelings of self-efficacy due to its intangible nature. Surveys are often susceptible to reporting bias as a result and provide less than optimal results.
- Strength is dependent on situations and conditions
The strength of self-efficacy beliefs can often vary depending on situations and conditions. This means they can be hard to accurately measure—particularly when considering different populations.
How the Self-Efficacy Theory Works
Self-efficacy theory is a psychological concept that explores an individual’s belief in their capability to act in ways essential to reach desired goals. This belief can be a powerful determinant of how people approach tasks, handle challenges, and persist in the face of obstacles. Individuals with high self-efficacy are more likely to set ambitious goals, persist in the face of challenges, and recover from setbacks.
Self-efficacy beliefs determine how much effort they put into completing the task, how well they focus, and the strategies they employ to reach success. For example, someone with a high self-efficacy belief may see failure as an opportunity to learn and grow, while someone with low self-efficacy may give up more quickly when obstacles arise.
The theory emphasizes the importance of four sources of self-efficacy: mastery experiences, vicarious experiences, social persuasion, and emotional and physiological states.
- Mastery experiences involve the acquisition of skills and the development of confidence through repeated success.
- Vicarious experiences refer to the observation of others successfully completing tasks.
- Social persuasion involves the encouragement and feedback of others.
- Emotional and physiological states refer to how physical and emotional states can impact self-efficacy beliefs.
Click to read on about the importance of 4 sources of self-efficacy in an interesting way!
The theory promotes techniques to enhance self-efficacy, which includes celebrating successes, making positive affirmations, staying motivated, and seeking out supportive environments. By fostering high levels of self-efficacy, individuals can increase their chances of success and enhance their well-being.
Self-efficacy beliefs determine how much effort they put into completing the task, how well they focus, and the strategies they employ to reach success. For example, someone with a high self-efficacy belief may see failure as an opportunity to learn and grow, while someone with low self-efficacy may give up more quickly when obstacles arise.
Factors including culture, environment, gender, prior experience, and social influences can all affect these beliefs over time. Ultimately, this theory helps individuals become aware of their capability and make better decisions connected to performance goals.
By evaluating these four sources of information (mastery experiences, vicarious experience, verbal persuasion, and physiological arousal), an individual can build or decrease their self-efficacy beliefs related to a given task and thereby drastically impact their behavior by creating either a positive or negative outcome.
Mastering these four sources of information should provide an individual with enough evidence to produce desired outcomes.
Applying Self-Efficacy Theory in Coaching
Applying Self-Efficacy Theory in coaching can help people reach their goals more effectively. Coaches can use techniques such as positive feedback, goal setting, and problem-solving to increase athletes’ self-efficacy and enhance their performance.
Coaches should ask questions that target athletes’ thoughts about their abilities and encourage them to be active participants in the decision-making process.
Moreover, the coach should assist enough for the athlete to stay motivated yet not so much that it hinders their autonomy. Understanding Self-Efficacy Theory is important for any coach or trainer who works with athletes to help them achieve excellence.
By helping the person develop these skills, coaches can create an environment that allows the client to experience successes and learn to apply them to different tasks. Through techniques like positive social comparison and mental rehearsal, coaches help clients increase their sense of self-efficacy, which leads to more successful outcomes.
When used properly in conjunction with other forms of therapeutic intervention, the self-efficacy theory has proven to be highly effective at helping those looking for increased accomplishments.
Conclusion
After researching and examining the self-efficacy theory, we can confidently say that it is an effective tool for improving self-efficacy and achieving the desired goals. Not only does the theory provide insight into how one’s beliefs about their capabilities affect their behavior. It also provides a variety of practical strategies—like mastery experiences and verbal persuasion—to learn to trust in oneself and reach new heights.
In conclusion, Albert Bandura’s self-efficacy theory plays a vital role in how people evaluate their strengths and weaknesses when it comes to achieving goals.
It encourages us to focus on our existing skills, while also striving to broaden our capabilities. With these insights in mind, we can tap into our inner reserves of motivation and courage, inspiring ourselves forward on the path toward our dreams.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the examples of the Self-Efficacy Theory?
According to the self-efficacy theory, an individual gains self-efficacy by monitoring their progress, receiving effective feedback on past experiences, comparing themselves with others’ successes, and believing they can successfully control a situation.
For example, if a person has high self-efficacy when it comes to public speaking, they will be more willing to take challenges and risks associated with it.
Similarly, someone with low self-efficacy will find it difficult to make decisions or take risks because of negative beliefs about personal abilities. As illustrated by these examples, self-efficacy is a powerful predictor of attitude and behavior change.
What are the characteristics of Self-Efficacy Theory?
Self-efficacy theory believes in one’s ability to take action is the foundation of the Theory, which has four primary characteristics.
1.These are the perceptions that an individual has of their capabilities, based on past experience.
2.The understanding that difficult tasks are possible to accomplish with effort.
3.Adjusted expectations are dependent upon levels of task difficulty.
4.Beliefs in one’s ability to succeed despite any external difficulties or pressure.


ABOUT SAI BLACKBYRN
I’m Sai Blackbyrn, better known as “The Coach’s Mentor.” I help Coaches like you establish their business online. My system is simple: close more clients at higher fees. You can take advantage of technology, and use it as a catalyst to grow your coaching business in a matter of weeks; not months, not years. It’s easier than you think.
AS SEEN ON
0 Comment